Female Labrador Retrievers typically experience their first heat cycle between 6-12 months of age. The heat cycle recurs about every 6 months, lasting around 3 weeks. During this period, there are behavioral and physical changes – increased urination, swollen vulva, bloody discharge, and attraction of males. So lets learn all about when do labs go in heat, lab mating and much more.

Like humans, labs undergo specific biological changes known as “heat” or estrus during pregnancy. They become sexually active as early as 6 months. Large dog breeds have it as late as 2 years. Understanding when labradors go into heat is essential for pet owners. It helps them take proper care.
when do female labs go into heat ( First Heat Cycle)
A critical aspect of the dog’s reproductive cycle is when the labradors go into heat for the first season. It’s known as estrus. Female Labs experience their first heat cycle between six and twelve months. Like the Labrador retriever, a large dog breed may take longer.
On the contrary, smaller breeds tend to have their first heat earlier. However, the first season of heat can vary depending on the dog’s breed, genetics, and environment. Stress, nutrition, and exercise also influence the onset of the first season for other dogs.
how long are labs in heat?
Female labs go into heat for around three weeks. Although it can be as short as two weeks or as long as four weeks. The duration of first season of the lab heat cycle can vary. It is essential to closely monitor your lab during this time, especially if you have male labs.
how often do labs go into heat?
Age and seasons can impact the number of times labradors go into heat. Let us explore the answers to these questions in depth.

Age
The age of your female pet can play a significant role when they have their first heat. Age also affects how often the labradors go into heat.
Generally, a female pup will have its first labrador heat cycle at around six months. After this, they will typically have a heat cycle every six months.
However, as your pet ages, the frequency of labradors’ heat cycles changes. As your pet enters its senior years, it may experience fewer heat cycles or even stop cycling altogether.
It is a sign their reproductive system is slowing down and preparing for the end of their reproductive life. Doctors recommend not to breed female labradors until they reach at least two years of age as have not reached sexual maturity yet. Breeding too early can result in complications during pregnancy and birth.
Conception
Heat cycles are also directly linked to conception. Unspayed pets will go into heat to prepare for breeding. They are receptive to male pets and more vocal during this time. Keep your pet away from male pets unless you intend to breed them.
Not all pets will conceive when labradors go into heat. If you plan on breeding your pet, speaking with a veterinarian to understand the timing and signs of ovulation is essential.
Seasons
Unlike other dog breeds, labs do not have a specific breeding season. Labradors go into heat at any time, regardless of the season. Changes in daylight can sometimes affect a dog’s cycle. If you notice any changes in your dog’s cycle, consult your veterinarian.

Labrador breeding cycle
The breeding cycle of a labrador retriever is divided into four stages: the Proestrus stage, the Estrus stage, the Dioestrus stage, and the Anoestrus stage.
| Phase | Duration | Symptoms | What to do |
| Proestrus | 7-10 days | Swollen vulva, increased urination, restlessness | Keep your labrador away from male dogs |
| Estrus | 7-10 days | Vulva discharges clear, straw-colored fluid, receptive | Keep your labrador away from male dogs |
| Diestrus | 60 days | Decreased activity, nesting behavior, increased appetite | Provide a comfortable nesting area for your labrador |
| Anestrus | 120 days | No visible symptoms | Monitor your labrador’s behavior for any changes |
1. The First stage, or Proestrus stage
Proestrus is the first heat stage of the estrus cycle in females. The proestrus stage typically lasts about nine days in dogs but can range from 0 to 27 days. The ‘first heat phase’ duration can vary from one female dog to another. It’s normal for some dogs to have a longer or shorter first heat stage.
Hormonal Changes
During proestrus, the estrogen levels in the female dog’s body increase, causing the follicles to develop. The increased estrogen levels cause the vulva to swell and become more prominent. The dog may have a bloody discharge from the vagina.
Attracting Male Labs
A male dog is attracted to a female lab during the proestrus stage. It happens due to changes in the female’s scent and behavior. Female labs are not receptive to mating at this stage and may reject male labs’ advances.
- Swollen vulva: Your dog’s vulva will become swollen and may appear larger than usual.
- Vaginal bleeding: Your dog may experience vaginal bleeding during this stage, lasting for a few days or up to two weeks.
2. Fertile stage or Estrus stage
Estrus, also known as the “heat” cycle, is a crucial period in the reproductive cycle of female animals. This is when the female is receptive to the male, and mating can occur. Here are some essential facts:
- Discharge: Most dogs may have a bright or dark red bloody discharge during this stage.
- Attracting male labs: Your dog may become even more vocal and actively seek out a male dog for breeding.
- Accepting male dogs: Your dog may allow male dogs to mount her during this stage.
Duration and Behavioral Signs
- The stage typically lasts 9 days in most female labs but can vary from 4 to 24 days.
- The female exhibits behavioral signs such as restlessness, excessive licking, vocalization, and increased social interaction with males.
Fertile Period
- The fertile period occurs during estrus when the female can become pregnant. It begins a few days after the onset of estrus and lasts several days.
Physical Changes
- The enlargement of the vulva is seen. However, it softens a little, making it more pliable for mating.
- There is a decrease in blood in the vulvar discharge during estrus.
- Hormonal changes also occur. Estrogen levels begin to drop while progesterone levels start to increase.
3. Dioestrus stage
After the estrus stage, a female lab enters diestrus, where they are no longer receptive to a male dog. It is a non-receptive stage and lasts for approximately two months.
Progesterone levels fluctuate during diestrus.
During diestrus, estrogen levels in most female dogs are low, while progesterone levels fluctuate. Progesterone levels peak around three to four weeks after the start of diestrus and then decline to basal levels by the end of the stage. These fluctuations in progesterone occur regardless of whether or not the dog is pregnant.
- Decreased discharge: Your dog’s discharge will reduce during this stage.
- Decreased attraction to male dogs: Your dog will become less vocal and less interested in male dogs.
- Nesting behavior: Your dog may start to show nesting behavior, such as gathering blankets and toys.
Key Points:
- Lasts around two months.
- Progesterone fluctuations happen regardless of the dog’s pregnancy status.
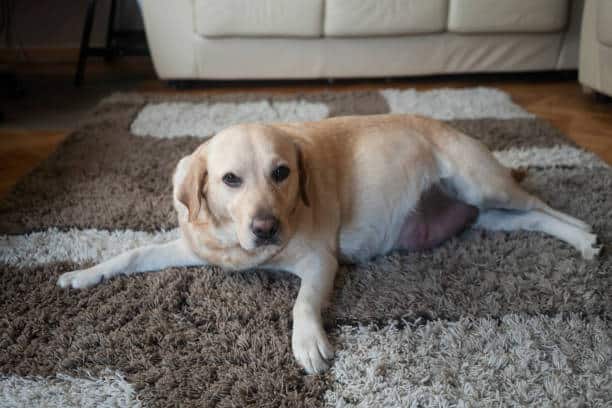

4. Resting stage or Anoestrus stage
Anestrus is a period in the reproductive cycle of female mammals that occurs between diestrus and the next proestrus. During this stage of the labrador’s heat cycle, the body prepares for the possibility of a future pregnancy.
Resting:
Your dog may rest more during this stage.
Absence of Swelling and Discharge
In Anestrus, the vulva is no longer swollen and has no vaginal discharge. It happens because the body is not currently preparing for ovulation or fertilization.
Preparation for Pregnancy
The body uses the time in anestrus to prepare the uterus for the subsequent possible pregnancy. It includes the development of the uterine lining and other physiological changes for a successful pregnancy.
Symptoms of a Labrador in heat
When it comes to breeding, it’s essential to understand the symptoms when labradors go into heat. By knowing these symptoms, you can provide better care and ensure a safe breeding process.
Swollen Vulva
One of the most noticeable symptoms of a Labrador in heat is a swollen vulva. The vulva is the external component of a female’s genitalia. It becomes larger and more prominent during the heat. The increased blood flow causes swelling to the area in preparation for mating.
Bleeding
Another symptom of a Labrador in heat is bleeding. Labradors will experience vaginal bleeding, lasting up to three to four weeks during the labrador heat cycle. If the female fails to conceive, shedding the uterine lining results in bleeding.
Increased Self Cleaning
Labradors in heat will also have an increased urge to clean themselves. It is due to the discharge present during this time. Keeping your Labrador clean is essential, as the discharge can attract bacteria and cause infections.

Behavioral Changes
Labradors in lab’s heat cycle also exhibit behavioral changes. They become more affectionate, clingy, or restless. They can display anxiety or nervousness due to the hormonal changes taking place.
Humping & Flagging
Labradors in heat may also resort to humping or flagging. Humping is common in male labs during mating, but female Labradors may also hump during the heat. Flagging is when the female dog raises her tail to one side to signal to potential mates.
Admirers
During heat, labradors are sexually active. Male labs become more interested in your female Labrador and linger around your property. Keep a close eye on your dog to ensure they do not mate with undesired partners.
Female labrador in heat signs ( Humping and flagging )
During the labrador retriever heat cycle, your dog may exhibit unusual, confusing, and alarming behaviors. One of the most common behaviors is humping and flagging.
Humping Behavior in Female Dogs
Humping behavior is not limited to male dogs. Females can also hump objects, other dogs, and even people. This behavior is an instinct triggered by various factors, such as excitement, anxiety, boredom, or hormonal changes during the labrador retriever heat cycle.
However, humping female dogs during the heat shows your dog is ready to mate. Humping during the dog’s heat period is not a sign of aggression, dominance, sexual orientation, or sexual maturity.

Flagging Behavior in Female Dogs
Another typical behavior during the labrador retriever heat cycle is flagging. This refers to raising the tail and exposing the vulva to attract males. Most female labrador retrievers in the heat period release pheromones that signal their readiness to mate.
Flagging is a way to advertise their availability. It is natural and instinctive. However, it can be dangerous as it can attract unwanted attention from male dogs and increase the risk of unplanned breeding.
How to Handle Humping and Flagging Behavior during Labrador Heat cycle?
If your female dog is humping and flagging, take measures to prevent unwanted mating. Some suggestions:
- Keep your dog on a leash or in a secure area to prevent her from running away or attracting unwanted attention.
- Consider using a dog diaper or sanitary pad to prevent the discharge from staining your furniture or carpet.
- Avoid taking your dog to public places where there are many male dogs.
- Spaying your dog can prevent flagging behavior altogether.
- Provide plenty of exercises and mental stimulation to avoid boredom and anxiety.
- Distract your dog with toys or treats to redirect her attention.
How to prevent your female dog from getting pregnant?
If you’re not planning on breeding your female lab, taking steps to prevent her from getting pregnant is essential.
Spaying
Spaying your female dog is the most effective way to prevent pregnancy. It involves removing your dog’s ovaries and uterus, eliminating the possibility of pregnancy. Not only does it prevent pregnancy, but it also reduces the risk of uterine infections and breast cancer.
Keep your dog supervised.
One of the most common reasons for unintended breeding is lack of supervision. If your female dog roams around freely and interacts with other male dogs, it increases the chances of mating. Therefore, keeping your female dog supervised at all times is crucial.
Keep male dogs away
Male dogs have a strong sense of smell and can detect when a female dog is in a heat cycle. Keep male dogs away from your female dog when she’s in heat. Restrict Your female dog indoors during the labrador retriever heat cycle to prevent unwanted mating.
Hormonal treatments
Various hormonal treatments, including injections, pills, and topical applications, prevent ovulation and pregnancy. Always consult your vet before opting for hormonal therapy, as it can have side effects.
Use a contraceptive injection.
Another option for preventing pregnancy in female labrador retrievers is a contraceptive injection. It contains a hormone that controls the dog from getting into heat and pregnancy. This is not the same as spaying, but it is effective for dogs that cannot undergo surgery.
Consider a dog chastity belt
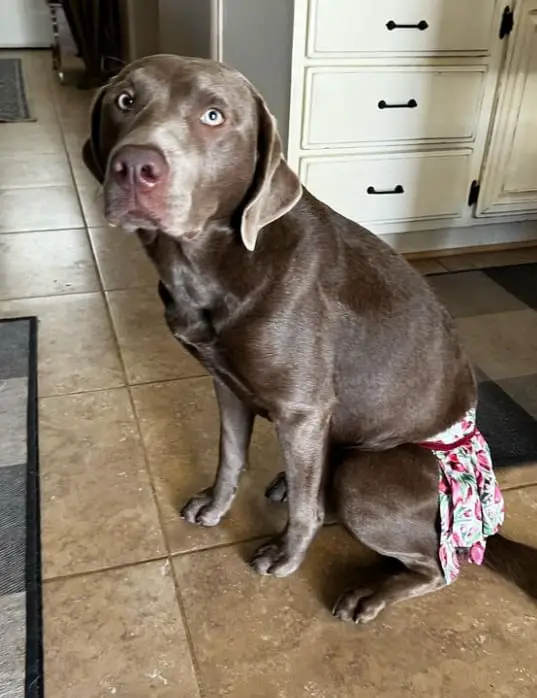
A dog chastity belt is worn around the female dog’s waist, preventing male dogs from mating with her. Finding a comfortable and well-fitting chastity belt is essential. It can cause discomfort and irritation if not fitted correctly.
Separating your own dogs while your dog is on heat
Being aware of the intricacies of dog mating is crucial for pet owners. One of the most critical considerations is how to separate your dogs when your female is in irregular heat cycles.
Will brother and sister dogs mate?
The short answer is yes. If you don’t separate them during your female labrador retriever’s heat cycle, there’s a high risk that they will engage in incestuous mating. It leads to health problems in resulting puppies, including genetic disorders and congenital disabilities.
Separating your male and female labrador retrievers during your female’s heat cycle is essential, especially if they’re related. Even if they’re unrelated, allowing them to mate leads to unplanned litters. It can be overwhelming and expensive.
What about the morning-after pill for dogs?
The morning-after pill, also known as Plan B, is a medication that can prevent pregnancy in human females. While a similar drug called the “morning after pill for dogs” is available for dogs, it is not a reliable form of birth control for dogs.
This pill is only effective if given within a specific time frame after mating and can have side effects. Recognizing that this pill cannot replace responsible pet ownership is crucial. Don’t depend on it as a typical birth control method.
when can a labrador get pregnant?
Choosing the right time to breed your female Labrador is key. Typically, the optimal time for the mating stage is between the 10th and 14th day of your female’s heat cycle. She’s most fertile during this time, and the chances of a successful pregnancy are highest.
It’s also crucial to ensure that both male and female domestic dogs are healthy and up-to-date on all vaccinations and preventative medications. A responsible breeder will select a suitable mate with the right temperament and genetic background to produce healthy, happy puppies.
When should you not mate your Female Labrador?
While breeding can be a rewarding experience, there are situations where it’s best to avoid mating your female Labrador. These include:
- Suppose your female has a history of health issues or genetic disorders. It could pass to her puppies.
- If your female is of very young age or old, safely carry and deliver a litter.
- Suppose you’re not prepared to provide proper care and attention to a litter of puppies. It includes finding suitable homes for them and providing necessary medical care.
- If your female has not undergone necessary health screenings.
- If your female has a temperament unsuitable for breeding, such as aggression or extreme shyness.
How To Care for Your Labrador In Heat Period?
The female dog needs extra attention and care during this heat to ensure her health and safety. Let us discuss some tips on how to care for your Labrador during the four stages.
Keeping your female Lab indoors
Always keep the female dog indoors. It will ward off unwanted pregnancies. It will also protect her from male dogs who can become aggressive and harm her. Create a cozy space for her in a quiet room, or use a crate where she can feel safe and secure.
Providing proper exercise and rest
Your female Lab may experience some discomfort and lethargy during labradors heat cycle. Giving her enough rest is essential. Avoid overexerting her with too much exercise. A daily walk is still essential, but keep it short and gentle.
Hide the trail of your female Lab
Female Labradors in heat release pheromones that attract male dogs. Keep your female Labrador safe by cleaning up after her when she goes out to do her business. Use special wipes that eliminate the pheromones or water and vinegar solution to clean up the area where she urinates.
Doggy Pants can be wonderful
Many brands design doggy pants specifically for female dogs during their heat cycle. They can help contain any bloody discharge and protect your furniture and floors from getting stained. They’re comfortable and come in different sizes and styles to fit your female Labrador.
Proper Nutrition
During her heat cycle, your female Labrador may experience some changes in her appetite. Providing her with a well-balanced diet that meets her nutritional needs is essential. You can also consider adding supplements like omega-3 fatty acids to support her health.
Gift her chews and toys
Your female Labrador may experience some mood swings during her heat cycle. Gifting her some new chews and toys can help keep her distracted and entertained. Choose toys that are durable and safe for her to play with.
How To Walk Your Dog in Heat cycle?
Walking not only does provide your dog with exercise but also helps them to relieve stress and anxiety. However, if your dog is in heat, be extra careful when taking them for a walk. Following are some tips on how to walk your dog in heat safely
Always have her on a leash
When your dog is in heat, she can become very excited and want to run around. Always keep them on a leash when taking them for a walk. Ensure they don’t run off or try to chase after a male dog in the area.
Avoid male dogs
Speaking of male dogs, avoiding contact with them when your dog is in heat. Male dogs can become very aggressive when they sense a female dog is in heat, leading to fights with your behaved girl.
Try to walk your dog in areas with no male dogs or keep it on a tight leash when passing by them.
Cover her tracks
When your dog is in heat, it will leave a scent trail wherever they go. It attracts male dogs, so covering their tracks is essential. Do this by taking different walking routes. Avoid areas your dog has previously marked and clean up any messes they may leave behind.
Are There Products Available To Help?
Thankfully, some products can alleviate the discomfort caused during the heat cycle. These products can make the experience less stressful.
Cooling Mats:
Heat cycles can cause your dog to feel uncomfortable and restless. A cooling mat on the dog’s bed can help your dog cool down and relax during these times.
Calming Supplements:
Behavioral changes during heat cycles are common, and your dog might become anxious or agitated. Calming supplements, such as chamomile or valerian root, can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
Heat Relief Spray:
A heat relief spray can help soothe your dog’s skin and relieve discomfort caused by the labrador heat cycle.

FAQs About Labrador’s Heat cycle
how long do labs bleed in heat?
Female labs usually bleed for one to one and a half weeks during the heat.
What is the best age to spay a female Labrador?
The best age to spay a female lab is around six months to prevent heat-related health issues.
When do male Labs go into heat?
Male labs do not go into heat. Only female labradors go into heat.
What to do when your dogs go into heat?
When your female labradors go into heat, keep them away from male labs, use dog diapers, and offer extra care.
Do dogs go through Menopause?
Dogs do not experience menopause, unlike human females.
At what age do Labradors mate?
Labradors can mate as early as eight months, but waiting until they are at least two years old is better.
when do labs have their first heat?
Labrador’s first heat cycle usually occurs between 6 to 12 months of age.
What is Split Heat?
A split heat occurs when a female dog initiates a lab heat cycle but fails to ovulate. She resumes the process later with a new set of follicles. It happens when the female interrupts the first heat cycle after standing but fails to ovulate. Subsequently presents herself for breeding during a second round of heat.
How Long Does A Labrador Bleed When In Heat?
A Labrador will bleed for 7 to 10 days during the proestrus stage of her heat cycle.
How Old Are Labs When They Go Into Heat?
The average age for a Labrador to go into heat for the first time is 6-12 months old. However, it can vary from dog to dog, and some Labs may go into heat as early as 4 months old or as late as 18 months old.
When Do Black Labs Go Into Heat?
The age at which black Labs go into heat is the same as when all Labradors go into heat, typically 6-12 months old.
When Do Labs Start Their Period?
Dogs do not have periods as humans do. They have a heat cycle divided into four stages: proestrus, estrus, diestrus, and anestrus. The proestrus stage is when the female dog will bleed.
When Do Chocolate Labs Go Into Heat?
The age is the same as when all Labradors go into heat, typically 6-12 months old.
How Long Does A Labrador Season Last?
The heat cycle of a female Labrador lasts 21-28 days. The proestrus stage lasts 9-10 days, the estrus stage lasts 5-7 days, the diestrus stage lasts 60-90 days, and the anestrus stage can last for several months or even years.
Author Profile
- Site Owner And Planning Specialist
-
Aritra, the founder of Labradorandyou.com, is a lifelong dog lover whose passion ignited for Labradors for their loyalty and intelligence. With extensive research and personal experiences, Aritra has become a Labrador expert, offering a rich resource on the breed. Labradorandyou.com provides reliable, timely, and evidence-based information, including Labrador-specific product reviews, training techniques, and care tips.
Labradorandyou.com was born out of Aritra's passion and his desire to share his profound knowledge about the breed. The site serves as a comprehensive resource, offering a wealth of up-to-date information for Labrador owners and enthusiasts alike
Also by the author
-
 FAQNovember 17, 2023How To Adopt An Emotional Support Dog?
FAQNovember 17, 2023How To Adopt An Emotional Support Dog?
-
 Mix-BreedsNovember 16, 2023Red Labradoodle Ultimate Guide: Breed Facts, Care Tips
Mix-BreedsNovember 16, 2023Red Labradoodle Ultimate Guide: Breed Facts, Care Tips
-
 Top BreedersNovember 8, 2023Breeding Labradors: Everything You Need to Know
Top BreedersNovember 8, 2023Breeding Labradors: Everything You Need to Know
-
 FAQOctober 17, 2023Do Dogs Like Music? Researchers Say Yes! Find Out
FAQOctober 17, 2023Do Dogs Like Music? Researchers Say Yes! Find Out





